Introduction
When working with Django, it’s not uncommon to encounter errors that can cause frustration and hinder development progress. One such error is the “ModuleNotFoundError,” which occurs when Django fails to locate a required module or package. In this blog post, we will explore the ModuleNotFoundError in Django, understand its causes, and provide examples along with code solutions to handle this error effectively. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to troubleshoot and resolve this issue in your Django projects.
Understanding the ModuleNotFoundError
The ModuleNotFoundError in Django is raised when an imported module or package is not found in the Python environment. This error usually occurs due to one of the following scenarios:
- Missing or misnamed module: The module or package you’re trying to import may not exist or might have been named differently.
- Incorrect import statement: The import statement in your Django project may be incorrect, causing Django to fail in locating the required module or package.
- Dependency not installed: If you’re using a third-party library or package that is not installed in your Python environment, Django won’t be able to locate it.
Now, let’s dive into a few examples to better understand these scenarios and how to handle them.
Example Scenarios and Code Solutions
Scenario 1: Missing or Misnamed Module
Suppose you have a Django project where you’re trying to import a custom module called my_module.py within the app directory. However, when you run your Django application, you encounter a ModuleNotFoundError for my_module.
Solution:
- Verify that the
my_module.pyfile exists in the correct location (appdirectory in this case). - Ensure that the module is correctly named and does not contain any typos or capitalization errors.
- Check if the module is added to the Django app’s
INSTALLED_APPSsetting in the project’ssettings.pyfile.
Scenario 2: Incorrect Import Statement
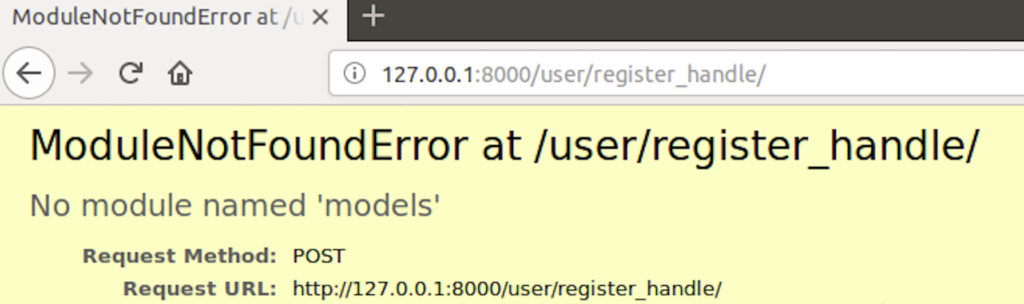
Let’s assume you are trying to import the models.py file from the my_app Django app into a view file called views.py. However, you receive a ModuleNotFoundError for the models module.
Solution:
- Double-check that the import statement in
views.pyis correctly referencing themodels.pyfile within themy_appdirectory. - Ensure that the module is correctly named and there are no typos or capitalization errors in the import statement.
- Verify that the
my_appDjango app is included in theINSTALLED_APPSsetting in the project’ssettings.pyfile.
Scenario 3: Dependency Not Installed
Suppose you’re using a third-party package, such as django-ckeditor, in your Django project, but you encounter a ModuleNotFoundError for this package.
Solution:
- Ensure that you have installed the
django-ckeditorpackage in your Python environment. You can use a package manager likepipto install it. - Double-check that the package is included in the
INSTALLED_APPSsetting in the project’ssettings.pyfile. - If you have recently installed the package, restart your Django server to ensure the changes take effect.
Conclusion:
The ModuleNotFoundError in Django can often disrupt the development process, but with a clear understanding of its causes and appropriate solutions, you can effectively handle this error. By addressing missing or misnamed modules, correcting import statements, and ensuring dependencies are properly installed, you can overcome the ModuleNotFoundError and continue building your Django projects without impediments.
Remember to double-check your code, verify the presence of required modules, and ensure the correct installation and configuration of dependencies to minimize the occurrence of this error. Happy coding with Django!
We hope this blog post has been informative and helpful in addressing the ModuleNotFoundError in Django. If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to leave a comment below.
Thank you for reading!